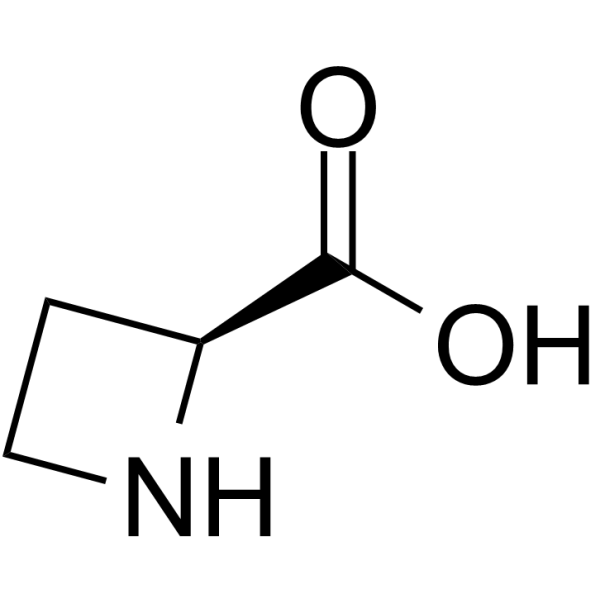
L-Azetidine-2-carboxylic acid
CAS No. 2133-34-8
L-Azetidine-2-carboxylic acid( L-2-Azetidinecarboxylic acid | (2S)-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid | L-Azetidine-2-carboxylic acid )
Catalog No. M29400 CAS No. 2133-34-8
L-2-Azetidinecarboxylic acid is a toxic proline analogue produced by members of the Liliaceae and Agavaciae families.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Azetidine-2-carboxylic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-2-Azetidinecarboxylic acid is a toxic proline analogue produced by members of the Liliaceae and Agavaciae families.
-
DescriptionL-2-Azetidinecarboxylic acid is a toxic proline analogue produced by members of the Liliaceae and Agavaciae families.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsL-2-Azetidinecarboxylic acid | (2S)-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid | L-Azetidine-2-carboxylic acid
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2133-34-8
-
Formula Weight101.103897094727
-
Molecular FormulaC4H7NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 100 mg/mL (989.12 mM)
-
SMILESOC(=O)[C@@H]1CCN1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
2-Deoxycytidine-5-mo...
2'-Deoxycytidine-5'-monophosphoric acid disodium (dCMP disodium) functions as an endogenous metabolite.
-
N6-(m-Methoxybenzyl)...
N6-(m-Methoxybenzyl)adenosine is an adenine nucleoside analog and a cytokinin derivative that can be used in agriculture to study branch growth and reproduction.
-
Pseudouridine
Pseudouridine is the most abundant modified nucleoside in non-coding RNAs. It enhances the function of transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA by stabilizing RNA structure.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


